City College, Fall 2018
Intro to Data Science
Week 4: Statistics and the Stories We Tell Ourselves
September 24, 2018Today's Agenda
- Types of Data
- Useful Statistical Distribution
- Important Summary Statistics
- Independence
- Key Theorems
Week 3 Recap
- Elements of the ETL Process
- Processing Tools: Luigi, Airflow
- Handling Missing Data: Drop, Impute
HW Recap
- Assignment 2 Notes
- There are cells other than code. Try markdown!
- Restart kernel and run all cells when you finish
- Answer all questions for full credit
- Collaboration is ok, copying is not. Disclose collaborators going forward.
- How was DataCamp?
- How do we feel about projects?
sta·tis·tics
noun
The practice or science of collecting and analysing numerical data in large quantities, especially for the purpose of inferring proportions in a whole from those in a representative sample.
Source
xkcd
Probability Distributions
A mathematical function that provides the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes in an experiment.
SourceBinomial

describes the likelihood for k successes over n trials with p probability of success where:

Wikipedia
Normal

Wikipedia
Uniform
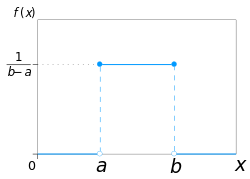
Wikipedia
Central Tendency
[1, 1, 1, 1, 6, 2, 4, 2, 9]
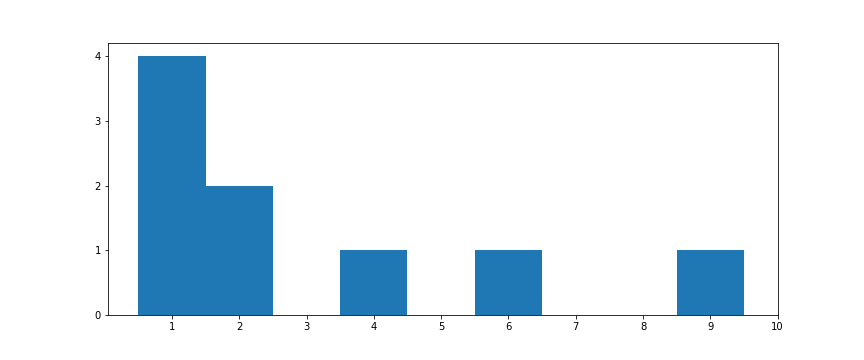
Central Tendency
Mean
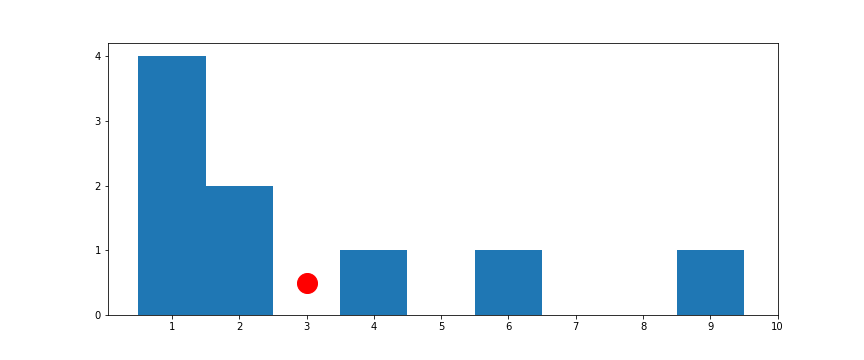
Central Tendency
Median
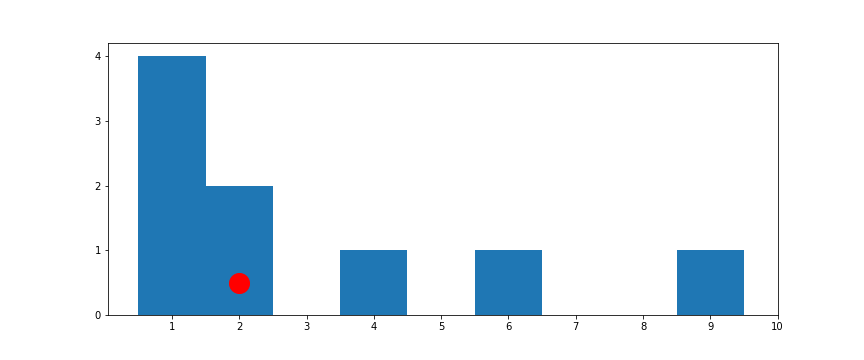
Central Tendency
Mode
Variation
Range
Variation
Min, Max
Variation
Variance, Standard Deviation

Variation
Percentiles
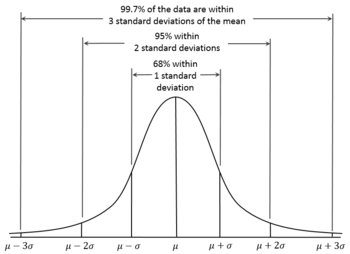
Dependence
How to describe the relationship between two distributions?
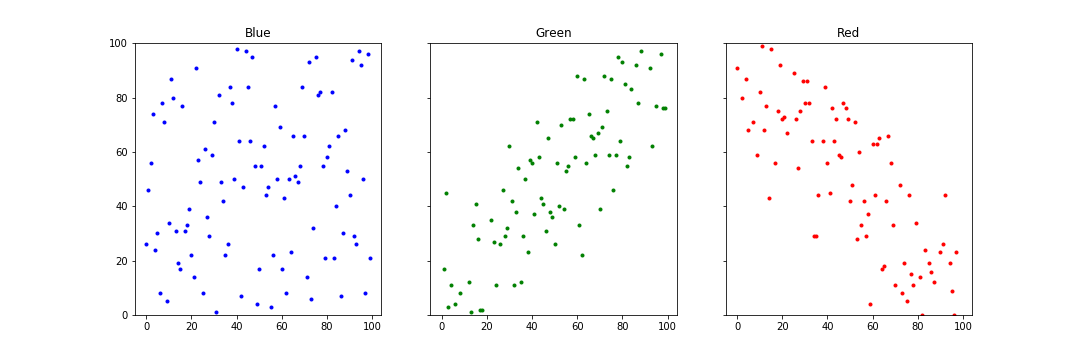
formal definition
Dependence
Covariance
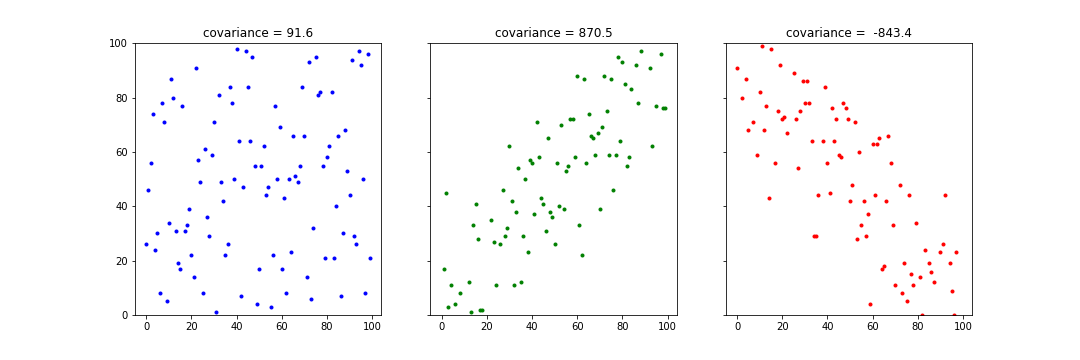
formal definition
Dependence
Correlation
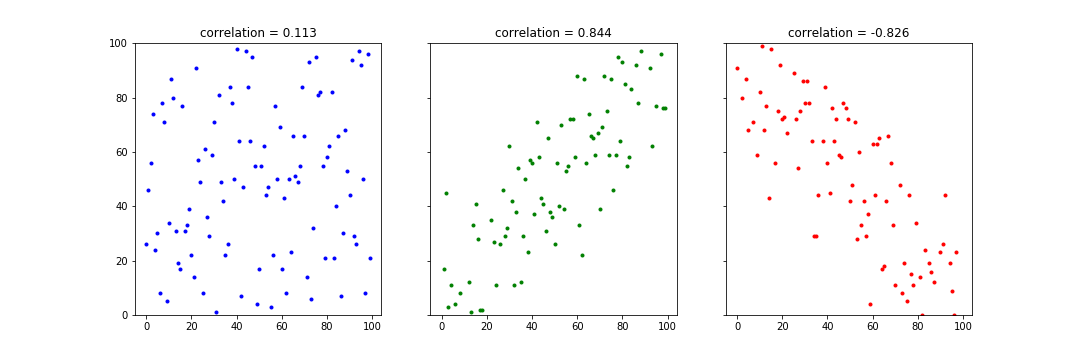
formal definition
Key Theorems
Law of Large Numbers
The average of the results obtained from a large number of trials should be close to the expected value, and will tend to become closer as more trials are performed.
Key Theorems
Central Limit Theorem
When independent random variables are added, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution (informally a "bell curve") even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed.


Wrap Up
- Types of Data
- Useful Statistical Distribution
- Important Summary Statistics
- Independence
- Key Theorems
Reference: Data Science from Scratch
Assignment 4: Due Monday, October 1 by 6:30pm
DataCamp's Statistical Thinking in Python (Part 2)
- The course should appear as assignment within your existing DataCamp account.
- Course takes 4+ hours, plan your time accordingly.