City College, Fall 2019
Intro to Data Science
Week 7: Trees and the Variance-Bias Tradeoff
October 21, 2019Today's Agenda
- Classification Review
- Linear vs. Nonlinear Classification
- Decision Trees
Semester Recap
- Loading and Transforming Data
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Linear Models for Regression and Classification
Project Teams
| Team | Member 1 | Member 2 | Member 3 | Member 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Team 1 | Ahsun | Phurpa | Sagun | Sanjay |
| Team 2 | Naeem | Ishraq | Garland | |
| Team 3 | Steven | Brian | ||
| Team 4 | Anthony | Jake | ||
| Team 5 | Charlie | Connie | Julia | Luis |
| Team 6 | Jin | Xin | Xiaohong | Hua |
| Team 7 | Enger | Jon | Kieran | Martin |
| Team 8 | Fayrouz | Frank | Ali | |
| Team 9 | Carlos | Oscar | Quetorah | Abigail |
| Team 10 | Dzhonibek | Hasibul | Abdur | |
| Team 11 | Runmin | Jie | Hongjie H. | Bida |
| Team 12 | Yorli | Inna | Lam | Michele |
| Team 13 | Jacinta | Andrew | Rabia | |
| Team 14 | Lizbeth | Kareem | Yu Xuan |
Data Science Models
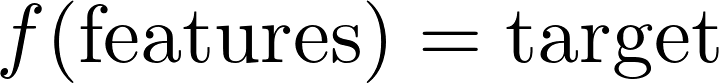
Linear models are most effective when the outcome can be modeled with a combination of coefficients of explanatory variables and the data is linearly separable.
Nonlinear models are better suited for outcomes which rely on interactions between different explanatory variables.
Linearly Separable Data
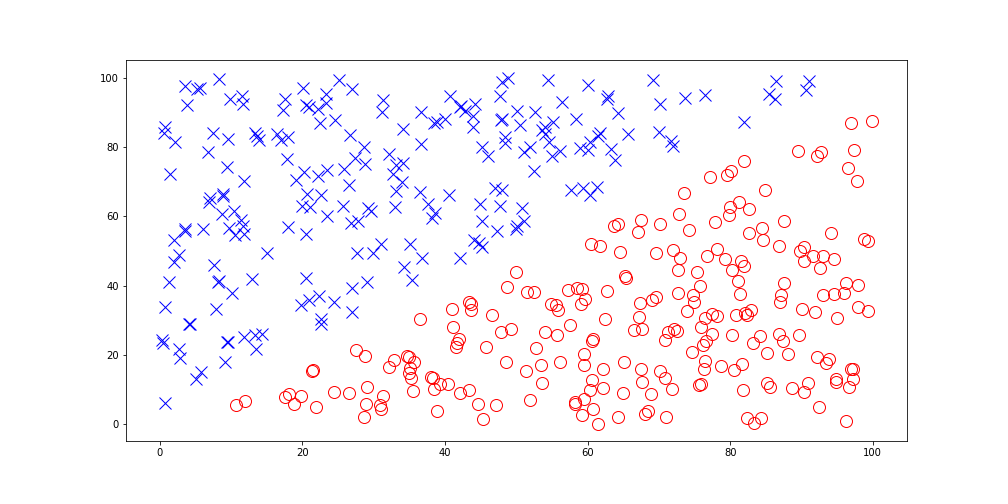
Linearly Inseparable Data
Titanic Disaster
2224 passengers, 710 survivors
Titanic Prediction Data Set
- Training set: 891 observations, 38 percent survival rate
- Features include: age, sex, socio-economic class, embarkation point, fare paid
- Rich potential for additional feature engineering
- Prediction goal: who survives?
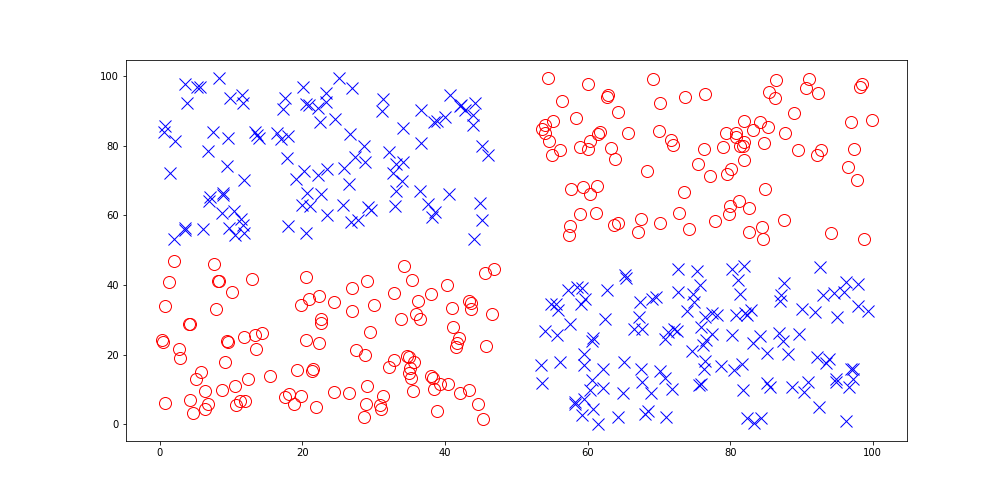
Survival Rates Among Subgroups

Survival Rates Among Subgroups
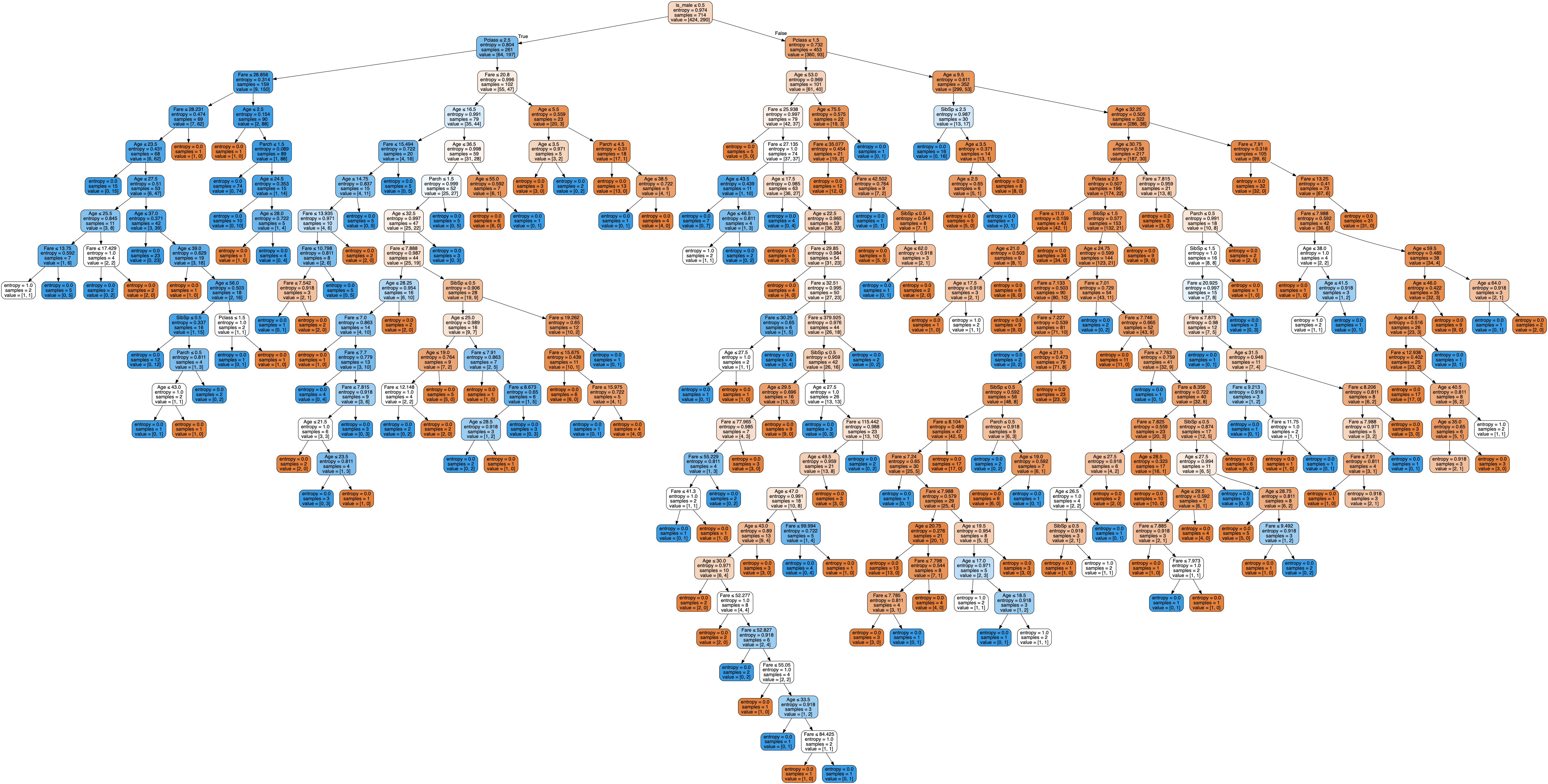
Branching a tree relies on a greedy heuristic, typically entropy.

Computers Make Branching Easy
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
An ideal model that both accurately captures the regularities in its training data, but also generalizes well to unseen data. Unfortunately, it is typically impossible to do both simultaneously.
Source.
How do we prevent unnecessary splits?
Hyperparameters: values set before the learning process to avoid overfitting.
Common decision tree hyperparameters:
- max_depth
- min_samples_split
- min_samples_leaf
- max_features
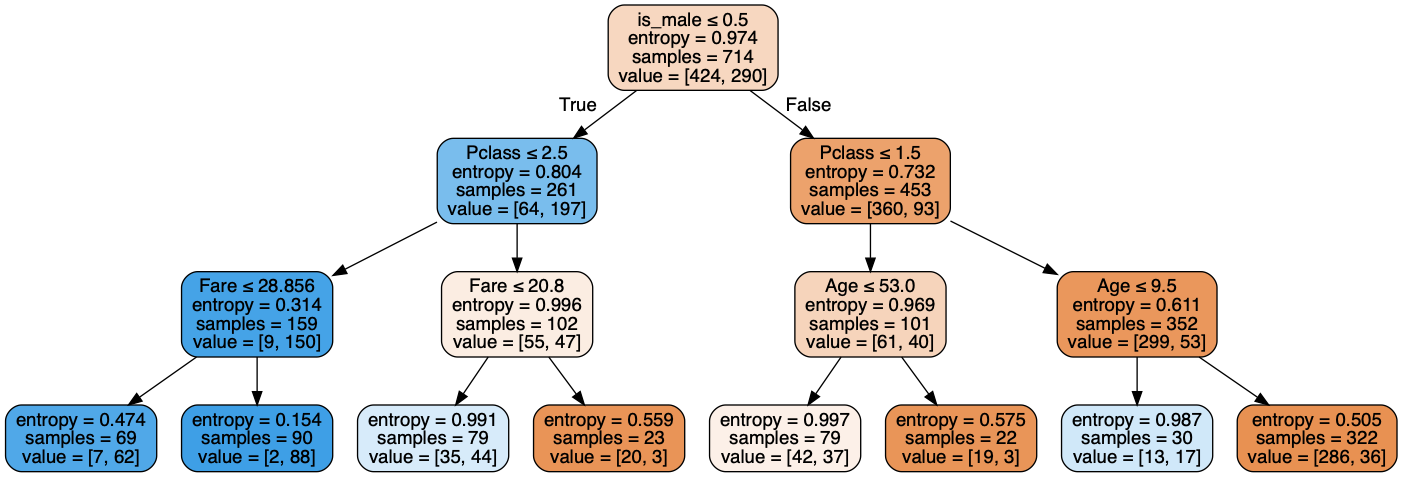
max_depth=3
max_leaf_nodes=6
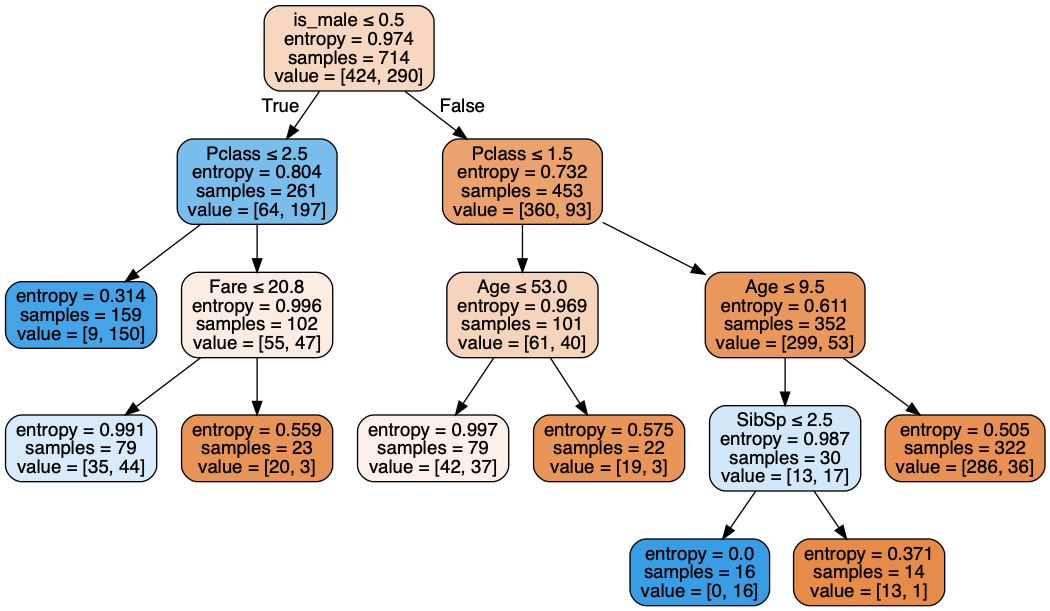
How do we choose hyperparameters?
Cross Validation

See here for a slightly deeper discussion.


Assignment 7: Due Monday, November 4 by 6:30pm
DataCamp's Deep Learning with PyTorch
- The course should appear collectively as assignment within your existing DataCamp account.
- Each section will appear separately and will be worth oen point toward the total grade for the homework.
- Course claims to take 5 hours, but I found it shorter than some of the past courses. Nonetheless, use your time wisely.